What is GPON?
Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) is a fiber-optic technology used for high-speed broadband access. It enables service providers to deliver internet, voice, and video services over a single fiber connection, offering efficient data transmission and scalability.
Key Takeaways
-
Fiber-based broadband for multiple services: GPON delivers internet, voice, and video over a single fiber connection, streamlining service delivery for both residential and business users.
-
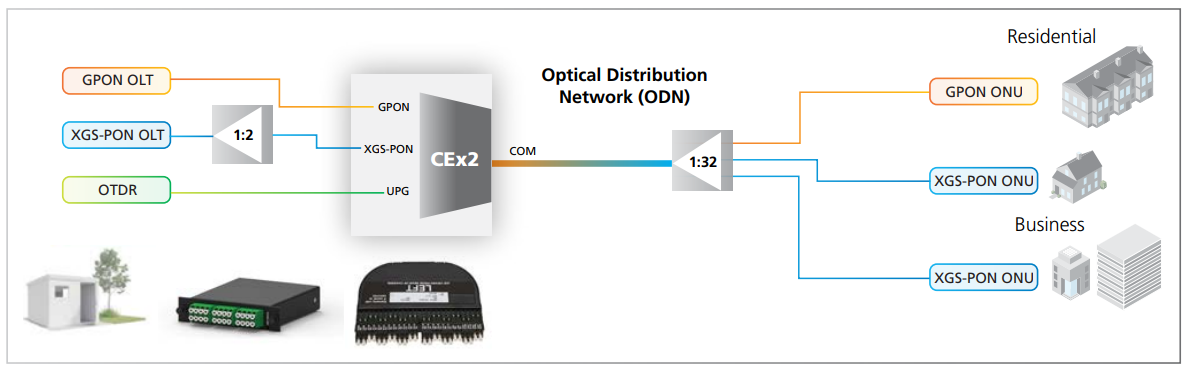
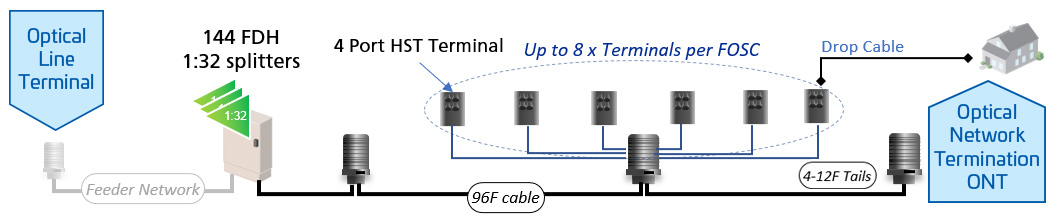
Efficient point-to-multipoint architecture: A central Optical Line Terminal (OLT) connects to multiple Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) using passive optical splitters, reducing the need for powered components in the field.
-
High-speed symmetrical performance: GPON supports downstream speeds up to 2.5 Gbps and upstream speeds up to 1.25 Gbps, offering reliable performance for modern digital applications.
-
Cost-effective and low-maintenance: The passive nature of the network minimizes operational complexity and maintenance needs, making it a practical choice for service providers.
-
Ideal for FTTH and FTTB deployments: GPON is widely used in Fiber to the Home and Fiber to the Building scenarios, helping expand broadband access while optimizing infrastructure efficiency.
How GPON Works
GPON operates using a point-to-multipoint architecture, where a single Optical Line Terminal (OLT) at the central office connects to multiple Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) at customer premises. It utilizes passive optical splitters to distribute signals, reducing the need for active components in the network.
Advantages of GPON
GPON provides high bandwidth, low latency, and cost-effective deployment. It supports data rates of up to 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.25 Gbps upstream, making it suitable for residential and business applications. Additionally, its passive nature minimizes maintenance requirements.
GPON in Network Infrastructure
GPON is widely used in Fiber to the Home (FTTH) and Fiber to the Building (FTTB) deployments. It enables service providers to expand broadband access while optimizing network efficiency and reducing operational costs.